Introduction: Drought is a prolonged period of abnormally low precipitation that can have far-reaching and devastating consequences for communities, agriculture, and the environment. In this educational post, we’ll explore the world of drought, including its causes, impacts, and strategies for mitigation and preparedness.
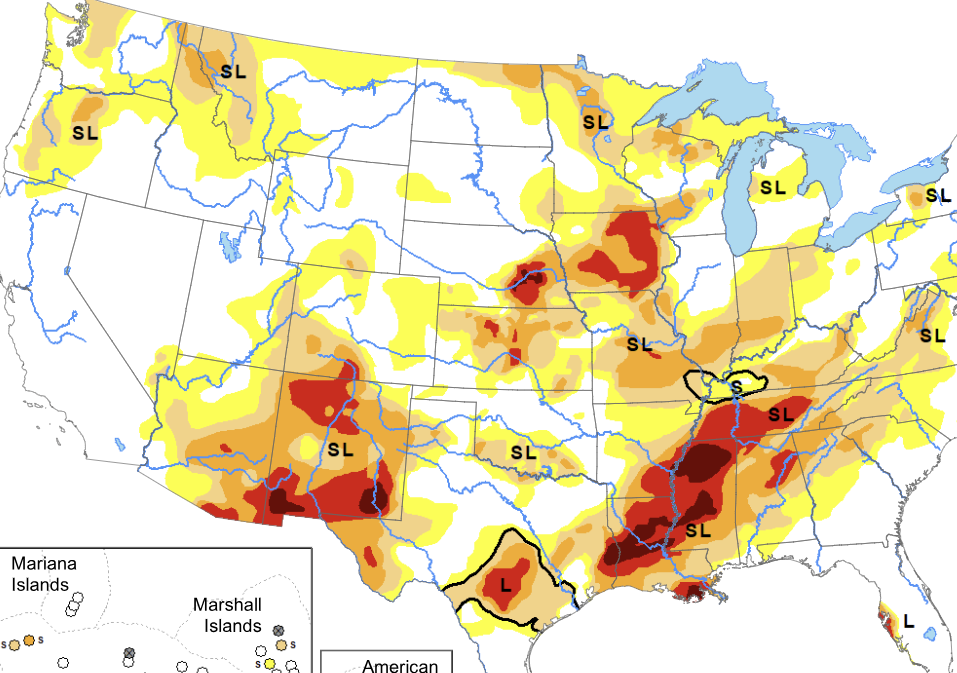
Defining Drought: Drought is a complex meteorological and hydrological phenomenon characterized by a deficiency in precipitation over an extended period, leading to water shortages. Droughts can vary in duration and intensity, from short-term dry spells to long-lasting, severe drought events. The US Drought monitor categorizes drought into four different categories.The D1 drought is the least intense level and D4 the most intense. Drought is defined as a moisture deficit bad enough to have social, environmental or economic effects. The list is:
- D0 (Abnormally Dry)
- D1 (Moderate Drought)
- D2 (Severe Drought)
- D3 (Extreme Drought)
- D4 (Exceptional Drought)
Causes of Drought: Droughts can have various triggers and contributing factors:
- Prolonged Lack of Rainfall: Extended periods of below-average precipitation are the primary cause of drought.
- High Temperatures: Elevated temperatures can lead to increased evaporation and transpiration rates, exacerbating dry conditions.
- Climate Variability: Climate patterns such as El Niño and La Niña can influence precipitation patterns and contribute to drought conditions.
- Human Activities: Deforestation, over-extraction of groundwater, and urbanization can alter local water cycles, contributing to drought.
Impacts of Drought: Droughts have far-reaching impacts on different aspects of society and the environment:
- Agriculture: Drought can devastate crops, leading to reduced yields, food shortages, and economic losses for farmers.
- Water Resources: Reduced water availability affects drinking water supplies, irrigation, and hydropower generation.
- Ecosystems: Drought can harm ecosystems, leading to wildfires, habitat destruction, and threats to wildlife.
- Economy: Drought can have a significant economic impact, affecting industries such as agriculture, tourism, and energy production.
- Health: Water scarcity can lead to health issues, including waterborne diseases and reduced access to sanitation.
Mitigation and Preparedness: Mitigating the impacts of drought and preparing for its occurrence are essential for resilience:
- Water Conservation: Implement water conservation practices in homes, businesses, and agriculture to reduce water consumption.
- Drought Monitoring: Use drought monitoring systems and early warning alerts to track developing drought conditions.
- Drought Preparedness Plans: Develop drought preparedness plans at local, regional, and national levels to respond effectively to water shortages.
- Water Management: Implement sustainable water management practices, including water recycling and groundwater recharge.
- Education and Awareness: Educate communities about drought risks and encourage water-saving behaviors.
Take Home: Drought is a complex and challenging weather phenomenon with severe consequences for communities and ecosystems. Understanding its causes, impacts, and mitigation strategies is essential for building resilience and adapting to changing climate conditions.
We hope this overview of drought has been informative and has highlighted the importance of preparedness and sustainable water management. If you have further questions or topics you’d like us to explore, please feel free to reach out. Stay informed, stay prepared, and stay resilient in the face of drought challenges!